Power Reserve in Watch Movements: What It Is and Why It Matters
Discover what power reserve means in watchmaking, how it functions in mechanical movements, and why it is essential for collectors and enthusiasts.

In the intricate world of horology, one technical term often emphasized among collectors and enthusiasts is the power reserve. Whether you're eyeing a manual wind timepiece or an automatic luxury watch, understanding the concept of power reserve is essential to appreciating its function and value. But what exactly does it mean, and why should it matter to you?
What Is Power Reserve?
The power reserve refers to the amount of time a watch can run on a full wind without requiring further winding or movement. In mechanical watches—both manual and automatic—it indicates how long the mainspring can supply energy to the movement once fully wound.
For instance, a watch with a 48-hour power reserve will continue to function for two full days after it has been fully wound, even if it is not worn or moved.
How Does It Work?
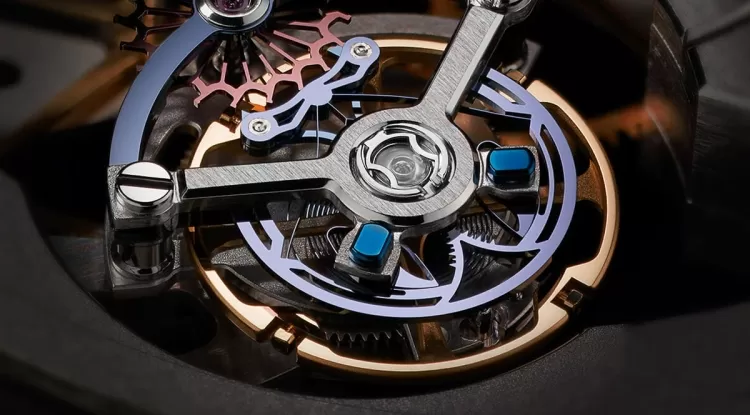
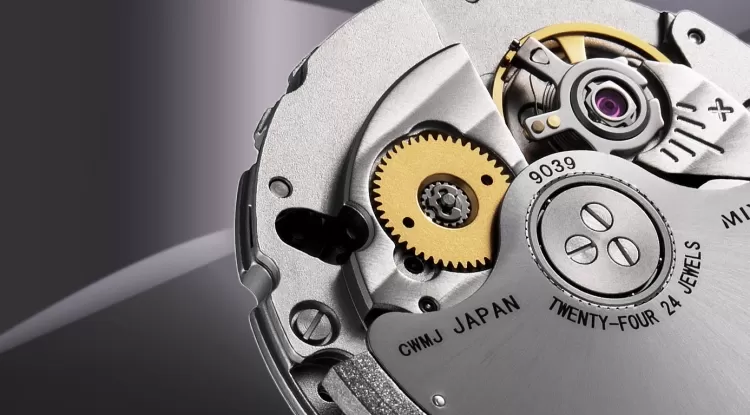
The heart of any mechanical watch lies in its mainspring, a coiled spring housed within a barrel. When wound—either manually via the crown or automatically through wrist movement—the mainspring stores kinetic energy. This energy is gradually released, powering the movement of the hands and complications.
The length and thickness of the mainspring, along with the design of the gear train and escapement, determine how long the energy will last—thus, the watch's power reserve.
Why Is Power Reserve Important?
- Convenience: A longer power reserve allows the watch to continue running while off the wrist, ideal for those who rotate between multiple timepieces.
- Travel-Friendly: During travel or periods when you can’t wind or wear your watch, a high power reserve ensures it remains accurate and functioning.
- Engineering Excellence: Watches with extended power reserves often showcase superior craftsmanship and innovation, enhancing their desirability and value.
- Functional Design: Some watches feature a power reserve indicator—a subdial or gauge that displays how much energy remains, helping the wearer decide when to wind it next.
Common Power Reserve Durations
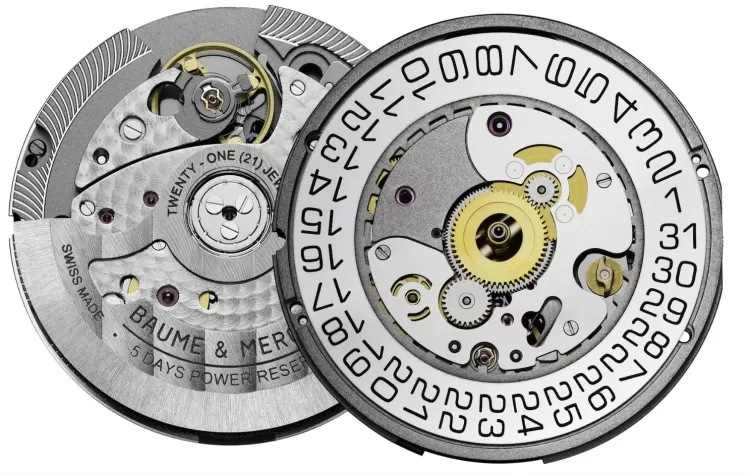
Most traditional mechanical watches offer between 38 to 50 hours of power reserve. However, high-end brands such as Panerai, IWC, and A. Lange & Söhne have models that offer power reserves extending to 7 days (168 hours) or more.
Some watches achieve this through a double-barrel system, using two mainsprings in series to store more energy, while maintaining a stable torque delivery to the escapement.
Quartz and Solar-Powered Watches
While power reserve is a concept mostly associated with mechanical timepieces, quartz watches also have a form of power reserve, determined by battery life. Typically, a standard quartz battery lasts 1–5 years.
In solar-powered watches, such as those by Citizen and Seiko, power reserve refers to how long the watch can run in complete darkness after a full charge—sometimes up to 6 months or more.
What's Your Reaction?