The Discovery and Function of Quartz Movements in Watches
Discover the history, mechanics, and significance of quartz watch movements. Learn how quartz technology revolutionized timekeeping with its precision, low maintenance, and affordability.
Quartz watch movements revolutionized the watch industry with their precision, durability, and affordability, changing timekeeping technology forever. Since their introduction, quartz mechanisms have become a mainstay in the world of horology, celebrated for their accuracy and relatively low maintenance requirements. This article explores the history, mechanics, and significance of quartz movements and how they continue to impact modern watchmaking.
The History of Quartz Movements
The development of quartz watch technology began in the 20th century, with early advancements in crystal technology paving the way. In 1927, Bell Telephone Laboratories produced the first quartz clock, using the piezoelectric properties of quartz to regulate time precisely. However, it wasn’t until 1969 that Seiko, a Japanese watchmaker, introduced the first commercially available quartz wristwatch, the Seiko Astron. This breakthrough marked the beginning of the “Quartz Crisis,” a period when quartz watches overtook mechanical watches due to their affordability and unmatched precision.
Quartz watches quickly gained global popularity due to their cost-effectiveness and accuracy, leading many traditional watchmakers to adapt and incorporate quartz movements into their collections.
What is a Quartz Movement?
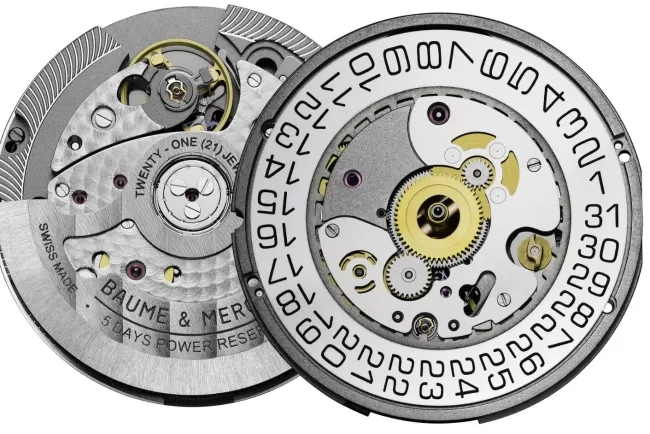
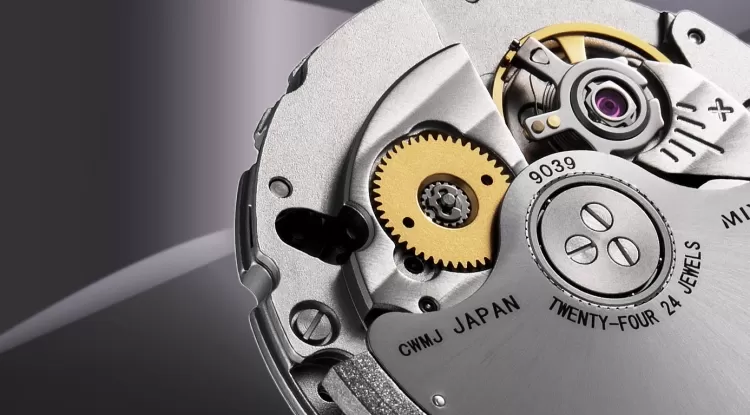
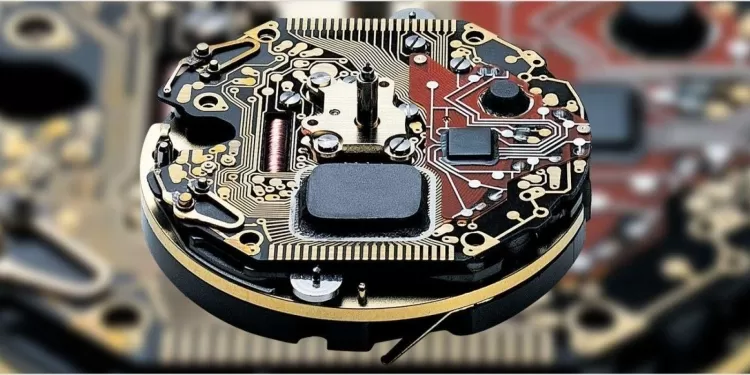
At its core, a quartz movement is a type of electronic oscillator regulated by a quartz crystal. This crystal, often shaped into a small tuning fork, oscillates at a precise frequency when exposed to an electric current. Quartz movements differ significantly from traditional mechanical watch movements, which rely on springs and gears. Instead, a quartz watch requires only a small amount of energy—typically provided by a battery—to drive its oscillation and timekeeping functions.
Quartz watches are well-regarded for their accuracy, typically deviating by only a few seconds per month, a vast improvement over the average accuracy of traditional mechanical watches.
How Quartz Movements Work
The fundamental principle behind quartz technology is piezoelectricity, a property in which quartz crystals generate a small electric charge when pressure is applied. In a quartz movement, the battery sends an electric current through the crystal, causing it to vibrate at a steady frequency—typically 32,768 times per second. This precise frequency is then measured by a circuit, which translates the vibrations into regular impulses, driving the hands of the watch in accurate, incremental movements.
Quartz movements can operate in two ways: analog and digital.
-
Analog Quartz Movements: In analog quartz watches, the impulses are transmitted to a small stepper motor, which moves the hands at regular intervals. This results in the characteristic "tick" of a quartz watch, contrasting with the sweeping motion of a mechanical watch.
-
Digital Quartz Movements: In digital quartz watches, the vibrations drive a digital display rather than physical hands, showing the time in numbers instead of with traditional hour and minute hands.
Benefits of Quartz Movements
Quartz movements offer several advantages over their mechanical counterparts:
- Accuracy: Quartz watches are incredibly precise, often losing only a few seconds per month.
- Durability: With fewer moving parts, quartz watches are generally more durable and less prone to damage from shock or wear.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Quartz movements are more affordable to manufacture than mechanical ones, making high-quality timepieces more accessible to a wider audience.
- Low Maintenance: Quartz watches require minimal maintenance aside from occasional battery replacement, making them convenient for daily wear.
Why Quartz Watches Remain Popular
Despite the resurgence of interest in traditional mechanical watches, quartz watches retain a strong presence in the market due to their reliability, precision, and affordability. Quartz movements are especially valued in fields requiring precise timekeeping, such as aviation, sports, and certain scientific applications.
Additionally, quartz watches have evolved aesthetically, with modern designs often incorporating advanced materials and innovative features, such as solar power, to extend battery life. Some high-end quartz models now rival mechanical watches in craftsmanship and luxury, bridging the gap between traditional and contemporary watchmaking.
The Impact of Quartz Movements on the Watch Industry
The advent of quartz movements fundamentally changed the watch industry by democratizing access to reliable timekeeping. Previously, high-accuracy watches were a luxury, reserved for those who could afford mechanical pieces. Quartz movements enabled watchmakers to produce affordable, high-quality timepieces that reached a broad market.
While the “Quartz Crisis” was initially seen as a threat to traditional watchmaking, it ultimately pushed the industry to innovate. Today, both quartz and mechanical watches coexist, each offering distinct benefits that cater to various tastes and needs in the watch community.
Future of Quartz Movements
The future of quartz movements lies in continual innovation, especially with the integration of solar power and hybrid designs that blend digital functionality with traditional analog displays. Advances in quartz technology have led to ultra-thin designs, eco-friendly power sources, and increased durability, ensuring that quartz watches remain relevant in a rapidly evolving world of wearable technology.
What's Your Reaction?